Diabetes Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Diabetes Management
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose). Effective management of diabetes is crucial to maintaining overall health and preventing complications. This guide provides essential information and strategies for managing diabetes effectively.
There are two main types of diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body does not produce insulin.
2. Type 2 Diabetes: A condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin.
Key Components of Diabetes Management
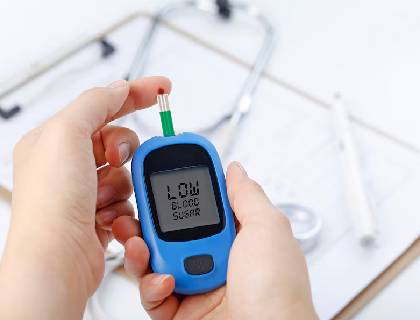
1. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regularly check your blood glucose levels to understand how your body responds to food, activity, and medication.
Use a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) for accurate readings.
2. Healthy Eating
Follow a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Monitor carbohydrate intake and consider working with a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan.
3. Physical Activity
Engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week.
Incorporate strength training exercises at least twice a week to improve insulin sensitivity.
4. Medication Management
Take prescribed medications as directed by your healthcare provider.
Understand how different medications work and their potential side effects..
5. Regular Check-ups
Schedule regular appointments with your healthcare team, including endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators.
Monitor for complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular issues.
6. Stress Management
Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation.
Ensure adequate sleep and consider counseling if needed.
Effective diabetes management requires a proactive approach that includes monitoring, healthy lifestyle choices, medication adherence, and regular healthcare visits. By taking control of your diabetes, you can lead a healthy and fulfilling life. For more personalized advice, consult with your healthcare provider or a diabetes educator.
